Base-and-Bounds
Base <= Base + Virtual Address < Base + Bounds
Virtual Address must be smaller than bounds
Example:
Base = 1000
Bounds = 500
→ Virtual Address = 300
Address is valid
Physical Address = 1000 + 300 = 1300
1000 <= 1300 < 1500
Linear Page Table
Gegeben:
- Address space size: 32m
- Physical memory size: 512m
- Page size: 64k
Page Table:
[90] 0x80000661
[91] 0x00000000
[92] 0x80001ad3
[93] 0x8000056b
[94] 0x80001eed
VA 0x005c5bff (decimal: 6052863) ⇒ PA or invalid address?
Lösung:
Page Size: 64k =
In Taschenrechner 6052863 Eingeben.
Ergebnis:
- 92 ist die Page Number
- 23551 ist der Offset
Page Table: [92] 0x80001ad3 1ad3 in Dezimal umwandeln: 6867. 0x8 bedeutet, dass die Seite im RAM liegt.
Also ist die virtuelle Adresse gültig und wir können die physische Adresse berechnen:
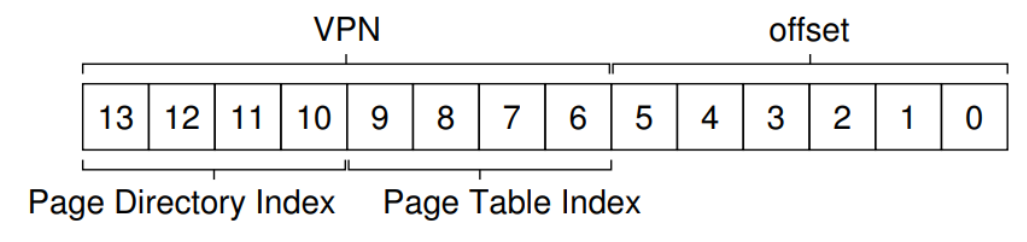
Multilevel Page Table
Page Fault Control Flow
Pseudo-Code:
VPN = (Virtual_Address & VPN_Mask) << SHIFT
(Success, TLB_Entry) = TLB_Lookup(VPN)
if (Success == true) { // TLB Hit
if (CanAccess(TLB_Entry.ProtectionBit) == false) {
Raise_Exception(Protection_Fault)
} else {
Offset = Virtual_Address & Offset_Mask
PhysAddr = TLB_Entry.PFN << SHIFT | Offset
Register = AccessMemory(PhysAddr)
}
} else { // TLB Miss
PTEAddr = PTBR + (VPN * sizeof(PTE))
PTE = AccessMemory(PTEAddr)
if (PTE.valid == false) {
Raise_Exception(Segmentation_fault)
} else if (CanAccess(PTE.ProtectionBit) == false) {
Raise_Exception(Protection_Fault)
} else if (PTE.present == false) {
Raise_Exception(Page_Fault)
} else { // Now can access
TLB_Insert(VPN, PTE.PFN, PTE.ProtectionBit)
RetryInstruction()
}
}The reason there is no explicit TLB valid bit check is that in a hardware-managed TLB, the TLB_Lookup(VPN) function only returns valid entries. If the entry were invalid, the lookup would fail, causing a TLB Miss, which then checks the page table for a valid mapping.
Deadlock
The four conditions for deadlock are:
- Mutual Exclusion: Resources cannot be shared.
- Hold and Wait: Processes hold resources while waiting for others.
- No Preemption: Resources cannot be forcibly taken from a process.
- Circular Wait: A cycle of processes exists, each waiting for a resource held by the next.